Koyo Technical Information
a. Handling of bearings
1) General remarks
- Bearings are highly precise products. Handle carefully to keep them free from dirt and dust as well as from impact.
- Use suitable handling jigs.
- Keep bearings away from moisture or perspiration to prevent corrosion.
2) Storing
Bearings are treated to prevent corrosion at the time of shipment. If they are stored unused for a long period of time, place on a shelf more than 30cm high from the floor, at 65% or less humidity and at 20. Keep them away from the strong sun. Do not place them near the window, where moisture condensation is likely.
3) Pre-installation preparations
Do not clean off anti-corrosion oil on the bearing when it is used under normal conditions. When it is used in an application of extremely high precision or at high speed, remove anti-corrosion oil with unpolluted cleaning oil, assemble quickly, and inject lubricant.
4) Inspection of shaft and housing
Before assembly, inspect the shaft and housing, and apply machine oil or other appropriate material to the mating surfaces of the individual components.
b. Mounting methods
b.1. Press fit of bearings with cylindrical bore bearings
| Mounting methods | Descriptions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
1) Using press fit(the most widely used method) |
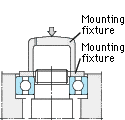
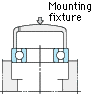
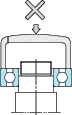
As shown in the Fig., a bearing should be mounted slowly with care, by using a fixture to apply force evenly to the bearing. When mounting the inner ring, apply pressure to the inner ring only. Similarly, in mounting the outer ring, press only the outer ring. |
||
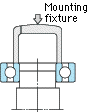 (Inner ring press fit) (Inner ring press fit) |
 (Outer ring press fit) (Outer ring press fit) |
 (Inner ring press fit) (Inner ring press fit) |
|
2) Using bolts and nuts (screw hole should be provided at the shaft end) |
If interference is required on both the inner and outer ring of non-separable bearings, use two kinds of fixtures as shown in the Fig. and apply force carefully, as rolling elements are easily damaged. Be sure never to use a hammer in such cases.
|
||
3) Using hammers(only when there is no alternative measure)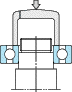 |
|||
b.2. Shrink fit of cylindrical bore bearings
| Shrink fit | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| 1) Heating in an oil bath
|
This method, which expands bearings by heating them in oil, has the advantage of not applying too much force to bearings and taking only a short time.
Notes:
|
| 2) Induction heater
|
|
Fig.12-1 Heating temperature and expansion of inner rings
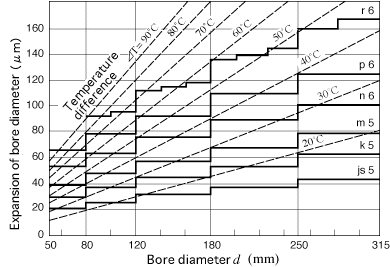
[Remarks]
1 Thick solid lines show the maximum interference value between bearings (class 0) and shafts (r6,p6,n6,m5,k5,js5) at normal temperature.
2 Therefore, the heating temperature should be selected to gain a larger “expansion of the bore diameter” than the maximum interference values.
c. Test run
To ensure that the bearing has been installed in a correct way, perform test runs to check out the following:
1) Rotational conditions
a) Knocking – Contaminants or damaged raceway may impair smooth rotation.
b) Excessive friction – Friction on the sealing device, error in mounting, or too small clearance may cause torque to become too high.
c) Fluctuations in running torque – Incorrect installation or error in mounting may make running torque uneven.
2) Abnormal noise
Check for any abnormal bearing noise by using a sound-locating bar or hearing aids. Because expertise is required to identify noise, it is desirable to have an experienced person to perform the check.
Table 12-2 Bearing noises, causes, and countermeasures
| Noise types | Causes | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclic | Flaw noise (similar to noise when punching a rivet) Rust noise (similar to noise when punching a rivet) Brinelling noise (Unclear siren-like noise) |
Flaw on raceway Rust on raceway Brinelling on raceway |
Improve mounting procedure, cleaning method and rust preventive method. Replace bearing. |
| Flaking noise (similar to a large hammering noise) | Flaking on raceway | Replace bearing. | |
| Not cyclic | Dirt noise (n irregular sandy noise) | Insertion of foreign matter | Improve cleaning method, sealing device. Use clean lubricant. Replace bearing. |
| Fitting noise (drumming or hammering noise) | Improper fitting or excessive bearing clearance | Review fitting and clearance conditions. Provide preload. Improve mounting accuracy. Replace bearing. | |
| Flaw noise, rust noise, flaking noise | Flaws, rust and flaking on rolling elements | Replace bearing. | |
| Squeak noise (often heard in cylindrical roller bearings with grease lubrication, especially in winter or at low temperatures) | If noise is caused by improper lubrication, a proper lubricant should be selected. In general, however, serious damage will not be caused by an improper lubricant if used continuously. | ||
| Others | Abnormally large metallic sound | Abnormal load Incorrect mounting Insufficient amount of or improper |
Review fitting, clearance. Adjust preload. Improve accuracy in processing and mounting shafts and housings. Improve sealing device. Refill lubricant. Select proper lubricant. |
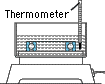
3) Abnormal generation of heat
After the start of operation, bearing temperature rises gradually and becomes constant within one to two hours. Temperature should be monitored and recorded continuously during operation for evaluation by comparison.
Trouble may cause irregular changes in temperature, such as a sudden rise.
Table 12-3 Causes of and countermeasures for abnormal temperature rise
| Causes | Countermeasures |
| Too much lubricant | Reduce lubricant amount. Use grease of lower consistancy. |
| Insufficient lubricant | Refill lubricant. |
| Improper lubricant | Select proper lubricant. |
| Abnormal load | Review fitting and clearance conditions and adjust preload. |
| Improper mounting (excessive friction) | Improve accuracy in processing and mounting shaft and housing. Review fitting. Improve sealing device. |
d. Maintenance and checking
To ensure that bearings can demonstrate their optimal performance and provide service over a long time, regular maintenance and inspection are required. Inspect uninstalled bearings by the following procedure:
1) Cleaning
When a bearing is uninstalled, check how much lubricant is remaining first. Clean the bearing with anhydrous, neutral light oil or kerosene. Warm alkalic solution or other material may be used as necessary. Clean the bearing preliminarily under cleaning oil, removing grease and sticking foreign matter with a brush or other tool. Do not rotate the bearing excessively during the preliminary cleaning.
After such foreign matter is removed, perform finishing cleaning while rotating the bearing slowly. Provide anti-corrosion treatment promptly when the cleaning is complete.
2) Checking
To determine whether the removed bearing can be used further, examine the bearing rings, rolling elements and cage carefully. If any of the damages shown in the Examples of Bearing Failures is found, use a new bearing.
e. Checking of bearings
1) Noise checking
Check for any abnormal bearing noise by using a sound-locating bar or hearing aids. Because expertise is required to identify noise, it is desirable to have an experienced person to perform the check.
Table 12-2 Bearing noises, causes, and countermeasures
| Noise types | Causes | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclic | Flaw noise (similar to noise when punching a rivet) Rust noise (similar to noise when punching a rivet) Brinelling noise (Unclear siren-like noise) |
Flaw on raceway Rust on raceway Brinelling on raceway |
Improve mounting procedure, cleaning method and rust preventive method. Replace bearing. |
| Flaking noise (similar to a large hammering noise) | Flaking on raceway | Replace bearing. | |
| Not cyclic | Dirt noise (n irregular sandy noise) | Insertion of foreign matter | Improve cleaning method, sealing device. Use clean lubricant. Replace bearing. |
| Fitting noise (drumming or hammering noise) | Improper fitting or excessive bearing clearance | Review fitting and clearance conditions. Provide preload. Improve mounting accuracy. Replace bearing. | |
| Flaw noise, rust noise, flaking noise | Flaws, rust and flaking on rolling elements | Replace bearing. | |
| Squeak noise (often heard in cylindrical roller bearings with grease lubrication, especially in winter or at low temperatures) | If noise is caused by improper lubrication, a proper lubricant should be selected. In general, however, serious damage will not be caused by an improper lubricant if used continuously. | ||
| Others | Abnormally large metallic sound | Abnormal load Incorrect mounting Insufficient amount of or improper |
Review fitting, clearance. Adjust preload. Improve accuracy in processing and mounting shafts and housings. Improve sealing device. Refill lubricant. Select proper lubricant. |
2) Temperature checking
After the start of operation, bearing temperature rises gradually and becomes constant within one to two hours. Temperature should be monitored and recorded continuously during operation for evaluation by comparison. Trouble may cause irregular changes in temperature, such as a sudden rise.
Table 12-3 Causes of and countermeasures for abnormal temperature rise
| Causes | Countermeasures |
|---|---|
| Too much lubricant | Reduce lubricant amount. Use grease of lower consistancy. |
| Insufficient lubricant | Refill lubricant. |
| Improper lubricant | Select proper lubricant. |
| Abnormal load | Review fitting and clearance conditions and adjust preload. |
| Improper mounting (excessive friction) | Improve accuracy in processing and mounting shaft and housing. Review fitting. Improve sealing device. |
3) Lubricant checking
This method detects abnormalities from the foreign matter, including dirt and metallic powder, in lubricants collected as samples. This method is recommended for inspection of bearings, which cannot be checked by close visual inspection, and large size bearings.

 Exclusive North American distributor for Gamet Bearing.
Exclusive North American distributor for Gamet Bearing.